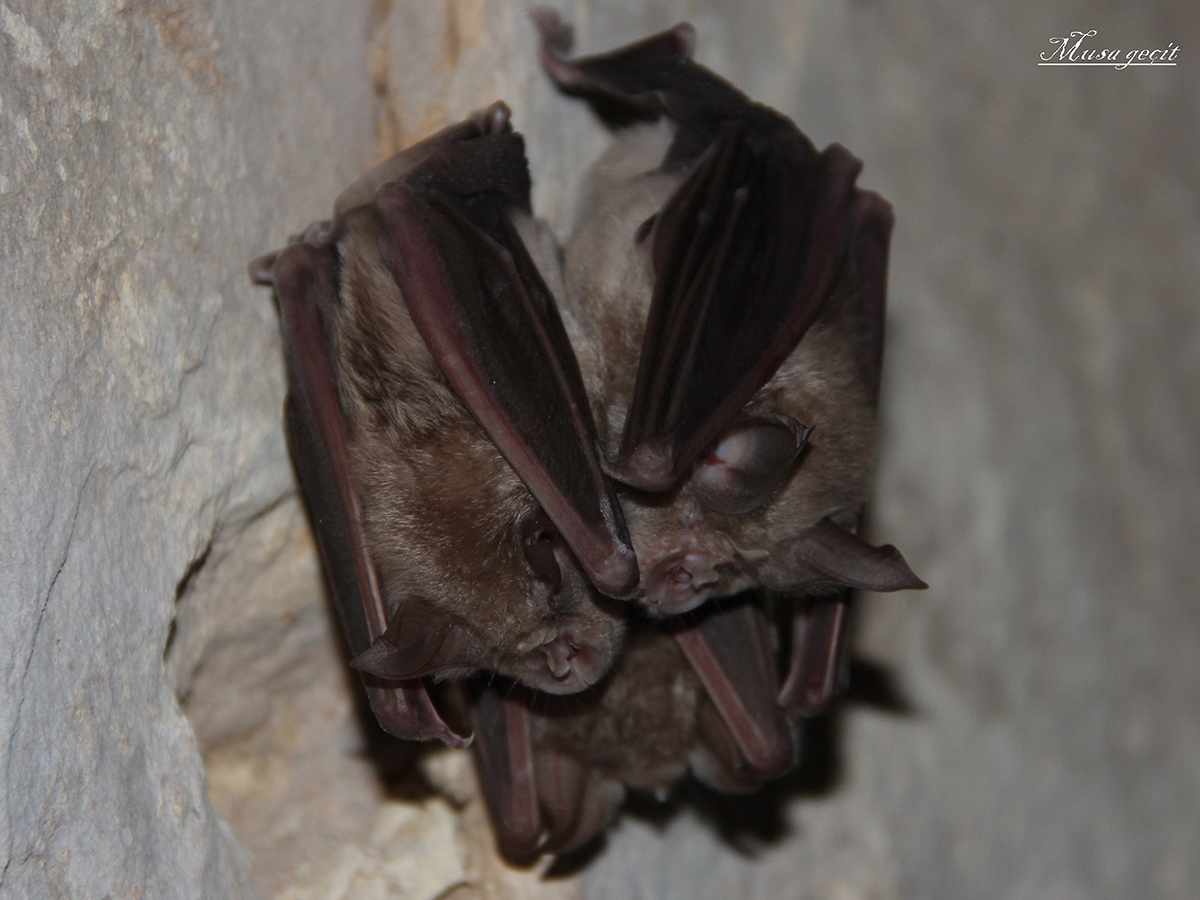

There are many different species of bats. Among them is the horseshoe bat. Its scientific name is Rhinolophus ferrumequinum. This species of bat is the largest of the genus Rhinolophus that inhabits Europe. In addition, it is also the most ubiquitous, as it prefers to live in wooded habitats rather than open biotopes. This species is typical of the southern Palearctic.
Like all Rhinolophus, the horseshoe bat emits ultrasound through the nose instead of the mouth. Along with the rest of these flying mammals belonging to the microchiroptera suborder, it does not have a swallow either.
Distribution of the horseshoe bat
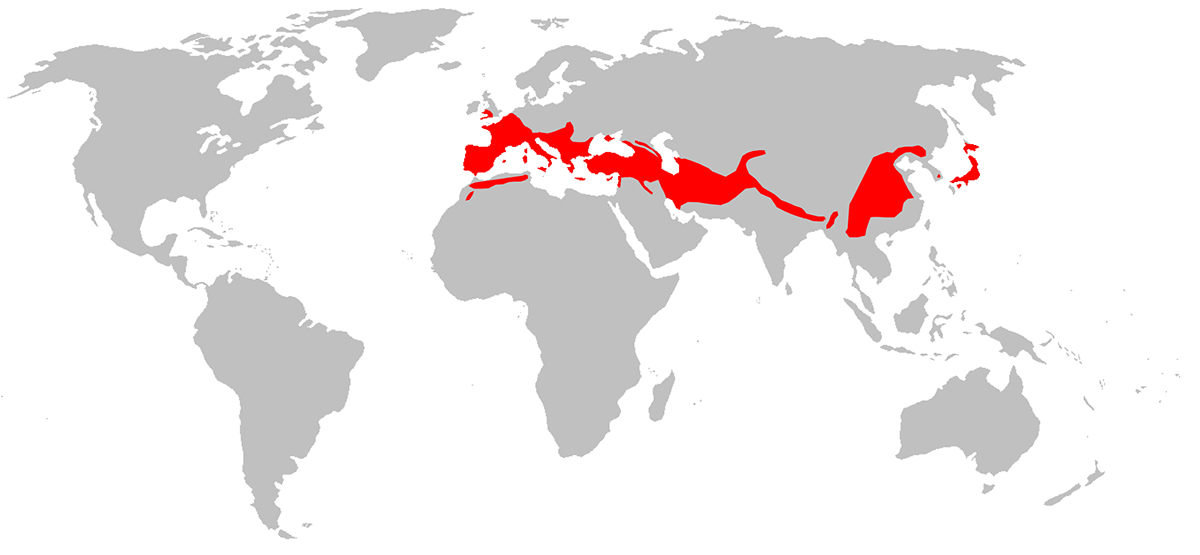
Rhinolophus ferrumequinum It is present in the southern Palearctic region. This includes countries from Morocco and the Iberian Peninsula to Japan. Within Europe, its northern limit is in the southwestern part of Great Britain to Greece. In the east, there are specimens of this animal in the Crimea.
Currently there is a population of around 50 thousand individuals in Spain. However, this number is decreasing over time in a general way throughout the Iberian Peninsula. The most affected areas are the east and the center of Spanish territory. Andalusia is the community with the highest number of horseshoe bats in the entire country. It is estimated that more than 11 thousand specimens of this species live there, which represents 23% of Spain. The decline of this population is moderate. It has been calculated that its decrease is 3,5% per year. Despite this, the Andalusian population of horseshoe bats is considered one of the healthiest in our country. Next to it are also those of Castilla-La Mancha, Extremadura and Castilla y León.
Horseshoe Bat Habitat
There is a wide variety of shelters used by Rhinolophus ferrumequinum. This animal is usually found in subterranean habitats during the winter. However, during its active season it is usually housed in cellars, attics and cavities. In general, their hunting areas are 200 and 1000 meters from the current refuge. Horseshoe bats use nocturnal roosts or "perches" for hunting. There they remain hanging until they locate their prey.
[related url=»https://infoanimales.net/murcielagos/myotis-myotis/»]
Its distribution ranges from sea level to an altitude of 1600 meters. The Rhinolophus ferrumequinum is a gregarious species. It can form colonies of up to 900 individuals. In addition, the horseshoe bat is sedentary and very faithful to its shelters that meet a series of appropriate conditions for the breeding season and hibernation.
Threats to the horseshoe bat

As Rhinolophus ferrumequinum has a very marked gergarism and a low regeneration capacity due to the fact that each female only has one calf per year, There are several factors that can be catastrophic for this species. The destruction or disturbances of the colonies result in the death of many specimens of these bats, from which they are not able to recover in a short time. The destruction or transformation of various habitats carried out by humans also destroys entire colonies of this species and many others. In addition, the massive use of forest insecticides is devastating for the horseshoe bat and other bats. In Israel, for example, the extreme fumigation of caves to combat the Rousettus aegyptiacus bat has brought it to the brink of extinction.
Within ecosystems all members play a role. Nature has created living beings within an order and balance that, when altered, can cause important changes and negative consequences. That's why we must be aware that ecosystems must be cared for, that implies taking care of the flora and fauna. If we continue to exterminate so many species of both animals and plants, we will end up extinct ourselves too.
The genus Rhinolophus
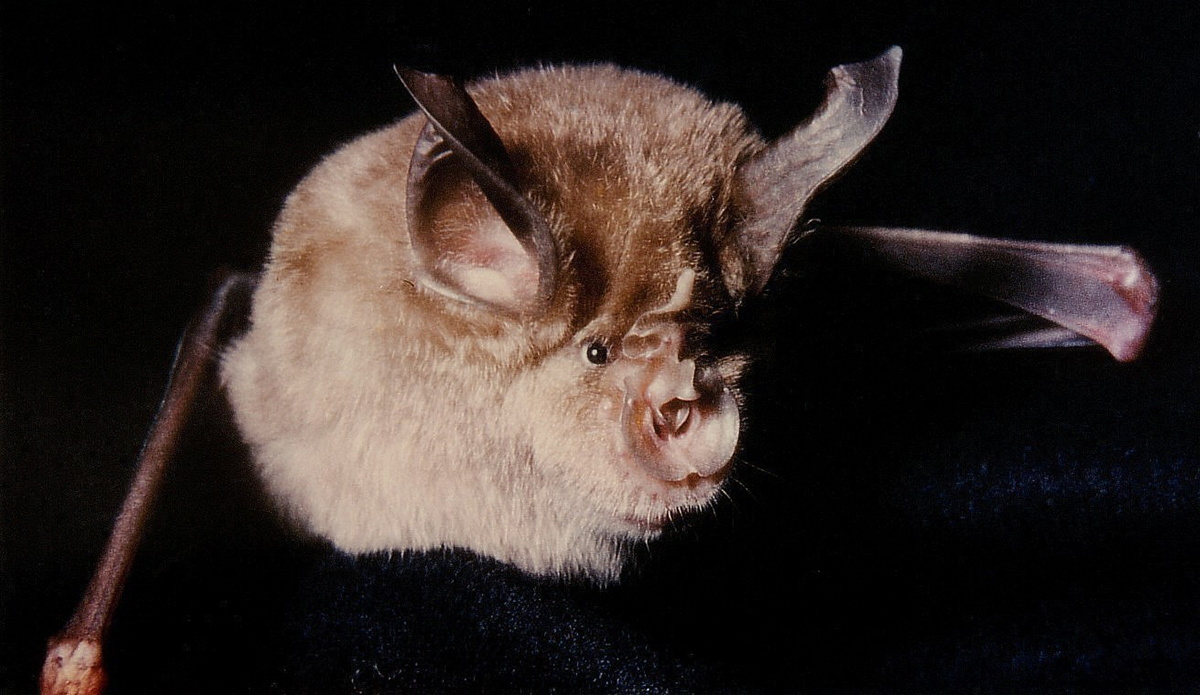

All rhinolophids or horseshoe bats They are insectivores that hunt and capture their prey in flight. In addition, they have very diverse lifestyle habits. While some species prefer to live in large colonies in caves, others inhabit hollow trees and some even sleep outdoors hanging from tree branches. Northern horseshoe bats typically hibernate during the coldest time of the year. A few species even hibernate in summer and at least one is migratory.
[related url=»https://infoanimales.net/murcielagos/murcielago-de-la-fruta/»]
A distinctive feature of rhinolophids is their multipart bumps on their noses. They are very similar to leaves with a horseshoe shape, hence their name. It is above all thanks to this trait that it is possible to distinguish rhinolophids from other bats with the naked eye.
In 2005, scientists identified a total of four species that carried a virus very similar to the SARS coronavirus. Those species are: R. sinicus, R. macrotis, R. pearsoni and R. ferrumequinum.